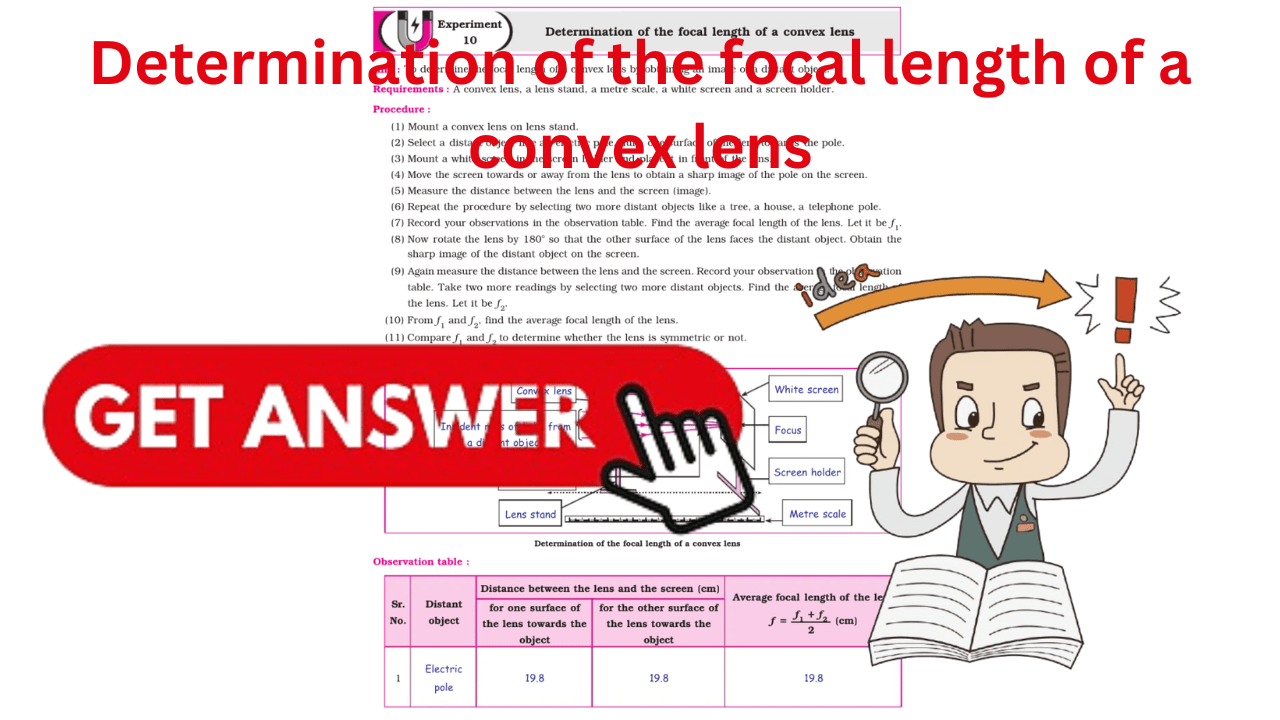
Standard 10th Science Experiment 9 Answer Solutions: Determination of the focal length of a convex lens Answer Solutions.
Aim :
To determine the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining an image of a distant object.
Requirements :
A convex lens, a lens stand, a metre scale, a white screen and a screen holder.
Procedure :
- Mount a convex lens on lens stand.
- Select a distant object like an electric pole. Turn one surface of the lens towards the pole.
- Mount a white screen in the screen holder and place it in front of the lens.
- Move the screen towards or away from the lens to obtain a sharp image of the pole on the screen.
- Measure the distance between the lens and the screen (image).
- Repeat the procedure by selecting two more distant objects like a tree, a house, a telephone pole.
- Record your observations in the observation table. Find the average focal length of the lens. Let it be f 1.
- Now rotate the lens by 180° so that the other surface of the lens faces the distant object. Obtain the sharp image of the distant object on the screen.
- Again measure the distance between the lens and the screen. Record your observation in the observation table. Take two more readings by selecting two more distant objects. Find the average focal length of the lens. Let it be f 2.
- From f 1 and f 2, find the average focal length of the lens. (11) Compare f 1 and f 2 to determine whether the lens is symmetric or not.
Diagram :
Label the various components in the given diagram.


Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct alternative and write its letter (A), (B), (C), (D) in the box :
1. The image formed by a concave lens is always .
(A) real, inverted and diminished (B) real, inverted and magnified (C) virtual, erect and magnified (D) virtual, erect and diminished
Answer: D
2. By using a , light rays incident on it can be converged.
(A) plane mirror (B) convex mirror (C) concave lens (D) convex lens
Answer: D
3. The incident ray parallel to the principal axis of a convex lens passes through after refraction.
(A) the optical centre of the lens (B) focus F2 (C) 2F2 (D) none of these
Answer: B