Standard 10th Science Experiment 9 Answer Solutions: Study of refraction of light through a glass prism Answer Solutions.
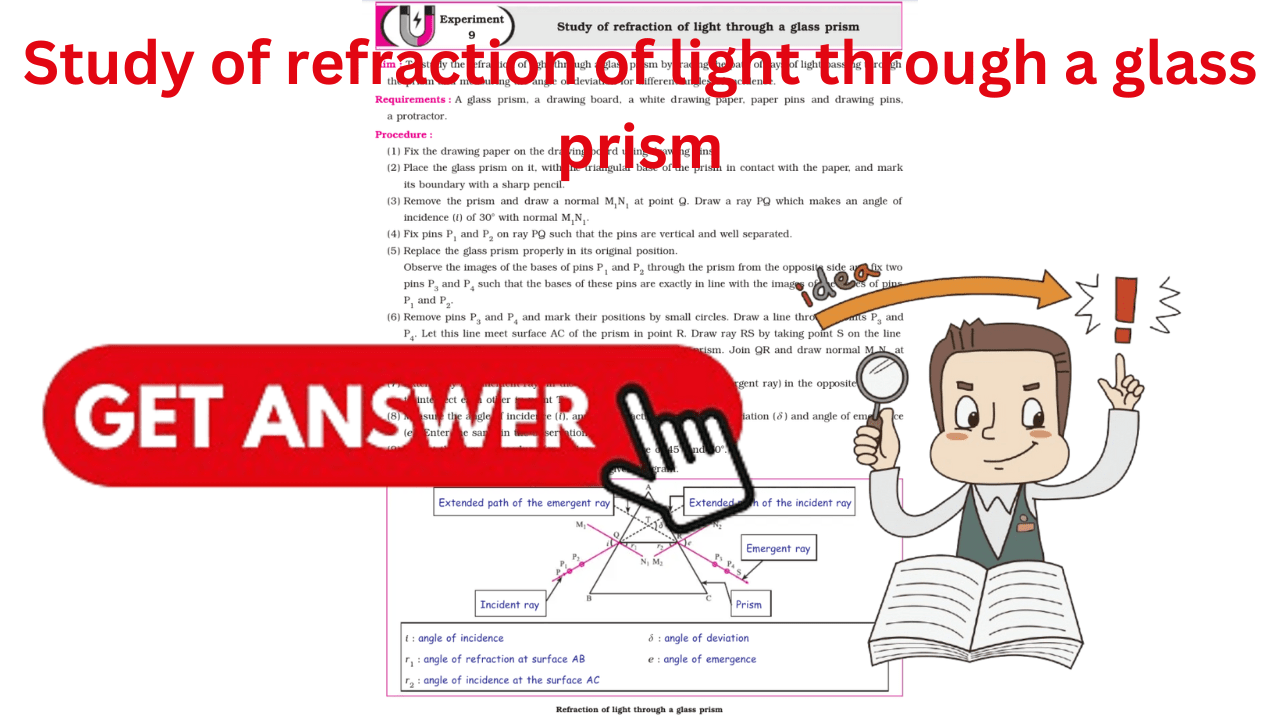
Aim : To study the refraction of light through a glass prism by tracing the path of rays of light passing throughthe prism and measuring the angle of deviation for different angles of incidence.
Requirements : A glass prism, a drawing board, a white drawing paper, paper pins and drawing pins,a protractor.
Procedure :
(1) Fix the drawing paper on the drawing board using drawing pins.
(2) Place the glass prism on it, with the triangular base of the prism in contact with the paper, and markits boundary with a sharp pencil.
(3) Remove the prism and draw a normal M1N1 at point Q. Draw a ray PQ which makes an angle ofincidence (i) of 30° with normal M1N1.
(4) Fix pins P1 and P2 on ray PQ such that the pins are vertical and well separated. (5) Replace the glass prism properly in its original position.Observe the images of the bases of pins P1 and P2 through the prism from the opposite side and fix twopins P3 and P4 such that the bases of these pins are exactly in line with the images of the bases of pinsP1 and P2.
(6) Remove pins P3 and P4 and mark their positions by small circles. Draw a line through points P3 and P4. Let this line meet surface AC of the prism in point R. Draw ray RS by taking point S on the line joining points P3 and P4. Remove pins P1 and P2 and the prism. Join QR and draw normal MN2 at point R. (7) Extend ray PQ (incident ray) in the same direction and ray RS (emergent ray) in the opposite directionto intersect each other in point T. (8) Measure the angle of incidence (i), angle of refraction (r1), angle of deviation (d) and angle of emergence(e). Enter the same in the observation table. (9) Repeat the above procedure for angles of incidence of 45° and 60°.
Diagram :
Label the various components in the given diagram.


Observation : The path of the ray for angle of incidence of 30° / 45° / 60° is PQRS.
Observation table :
| Angle of incidence (i) | Angle of refraction (r1) | Angle of deviation (d ) | Angle of emergence (e) |
| 30° | 20° | 43° | 73° |
| 45° | 30° | 37° | 60° |
| 60° | 38° | 40° | 40° |
Inferences :
(1) The angle of incidence (i)>the angle of refraction (r1).This means that when a ray of light travels from air to glass, it bends towards the normal.
(2) The angle of emergence (e)>the angler2. This means that when a ray of light travels from glass to air, it bends away from the normal.
(3) In general, the angle of deviation (d) depends on the angle of incidence (i). If the angle of incidence is gradually increased, starting from (say) 30°, initially d decreases as i is increased, becomes minimum for certain value of i and then increases as i is increased.
Precaution :
Pins should be fixed such that they are vertical and well separated.
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct alternative and write its letter (A), (B), (C), (D) in the box :
1. The change in the direction of propagation of light when it passes obliquely from one transparentmedium to another is called .
(A) dispersion (B) scattering (C) refraction (D) reflection
Answer: C
2. A ray of light gets deviated when it passes obliquely from one medium to another medium because .
(A) the colour of light changes (B) the frequency of light changes (C) the speed of light changes (D) the intensity of light changes
Answer: C
3. of light is responsible for twinkling of stars.
(A) Reflection (B) Internal reflection (C) Dispersion (D) Refraction
Answer: D
4. light is deviated the maximum in the spectrum of white light obtained with a glass prism.
(A) Red (B) Yellow (C) Violet (D) Blue
Answer: C
5. light is deviated the least in the spectrum of white light obtained with a glass prism.
(A) Red (B) Yellow (C) Violet (D) Blue
Answer: A